Regional Geography
of Vietnam
Outline
- Physical Characteristics
- Relative location
- Landscape and Physical
Environment
- Weather and climate
- Human Characteristics
- Population, Density and
Age/Sex characteristics
- Language and religion
- Cultural/ethnic groups
- Economic Characteristics
- Major economic
activities
- Imports and Exports
- GNP and GNP per capita
- References
Physical
Characteristics
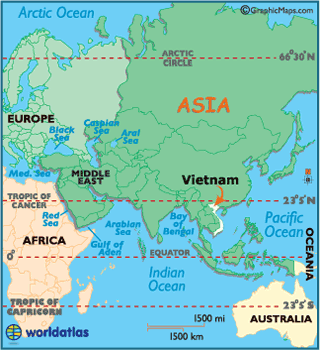
Vietnam
lies on the southeast corner of the continent of Asia. The country is found between
the Tropic of Cancer and the Equator. It is bounded on the northeast by the Gulf
of Tonkin, by the Gulf of Thailand on the southwest, and the rest of the coastline
being made up by the South China Sea. Neighboring countries include Cambodia at
the South West, Laos borders on the West just north of Cambodia, and on the north
of Vietnam is China. The total land area of Vietnam is 127,882 square miles,
which makes it the 65th largest country by area in the world
(Wikipedia).
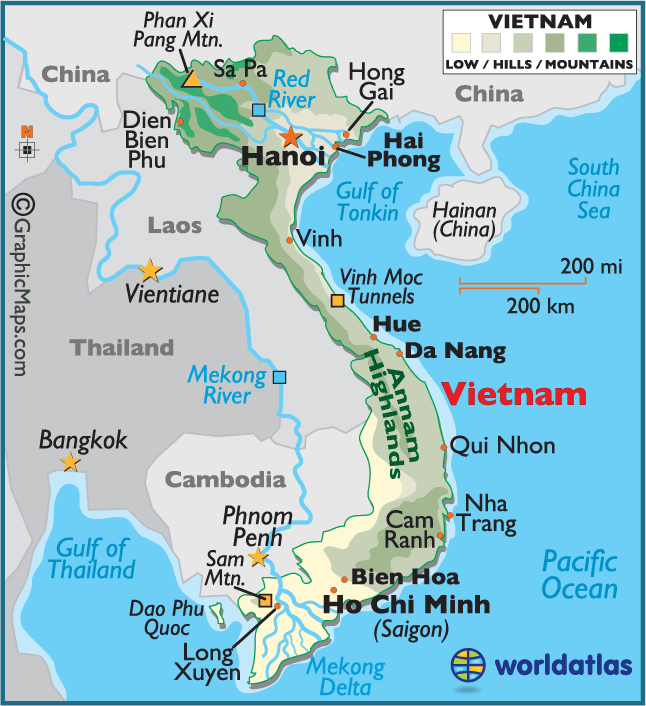
Nearly
50% of the border of Vietnam is coastline. The land extending inland from the
coastlines is lowlands that gradually becomes steeper. Areas in the southern
tip of the Mekong delta are entirely lowland while areas in the northern tip contain
mountainous areas, including Phan Xi Pang Mountain, the tallest in Vietnam standing
just above 10,000 feet. The country holds 2,360 rivers. Vietnam is very hilly with
less than 20% of the land being level. Parts of the country are very narrow,
being only 31 miles across from west to east around the center of the country. Ranked
16th in biodiversity in the world, Vietnam is home to 16% of the world’s
species (Wikipedia).
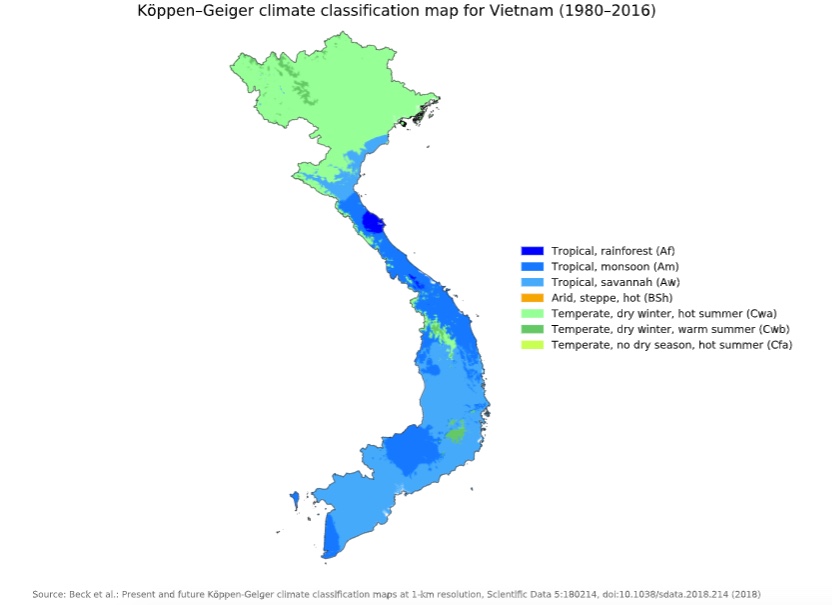
Vietnam
spans a great distance from north to south and because of this large variation
across latitudes the country’s weather and climate varies greatly. The north is
colder and is monsoonal with four seasons, while the south is tropical monsoon
and experiences wet and dry seasons. Temperatures vary from as low as the
record low of 21°F in a couple northern
provinces to the record high of 110° F in a southern province.
Average temperatures during winter across the country span from 36°F
- 79°F, while during the summer it is 77°F-
86° F. Average winter temperatures in the north are generally
below 68°F. Much of Vietnam receives about 55 inches to 94 inches of
rain every year, with somewhere from 80%-90% of that rain coming during the
rainy season. Some areas receive as little as 28 in per year, while others can
be as high as 197 in per year. (Climate
of Vietnam, Wikipedia)
Human
Characteristics
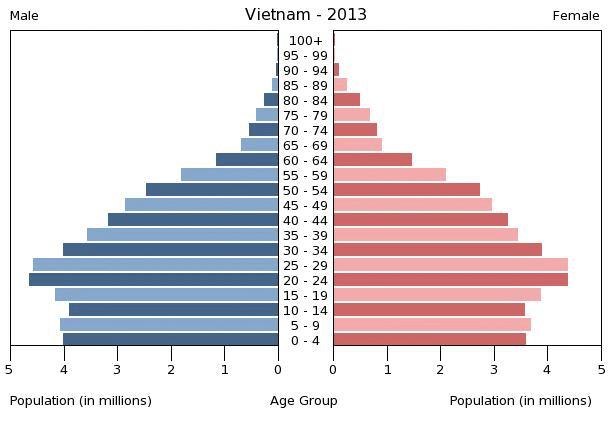
Vietnam
has a population of 95.7 million people. The country has a population density
of 1,367 people per square kilometer of arable land. About 23% of the
population is younger than 15 years old, while only 7% of the population is
older than 65 years. The average household size is 3.9 people (PRB database). Gender
demographics are nearly equal with 49.5% of the population being male and 50.5%
being female. The labor force is 28.5% urban and 71.5% rural (alotrip.com).
The
national language of Vietnam is Vietnamese. Most of the population speaks it,
but other languages are spoken as well mostly by minority groups. Other
languages spoken include: Hmong, Khmer, Cham, Chinese, Tay, Murong,
and Nung. French is also spoken by many educated
Vietnamese, while Russian, Polish, Czech, and German is still spoken by some
Northern Vietnamese that had ties with these countries during the Cold War. A
number of religions are practiced in Vietnam, with 73.2% practicing Vietnamese folk
religion or being not religious. Other religions practiced include Buddhism
(12.2%), Catholicism (6.8%), Caodaism (4.8%), Protestantism (1.5%), and Hoahaoism (1.4%) (Wikipedia).
There
are 54 different ethnic groups living in Vietnam. 85.7% of the population is
Vietnamese, with 53 other minority groups making up the rest. Other groups
include the Tai, the Murong, Hmong, Nung, Tay, and Khmer. Traditional Vietnamese culture focuses
on humanity and harmony, holding emphasis on community and family values.
Ancient cultures such as Khmer, Champa, and Sa Huynh have
traces of influence throughout Vietnamese culture, along with modern foreign
influences such as China and Western cultures (Wikipedia).
Economic
Characteristics
Vietnam
is a Socialist Republic with state run industries and utilizing “socialist-oriented
market economy” reforms which allow “free market zones” to attract foreign
investment. The currency of Vietnam is the dong. Agriculture has traditionally been
the bulk of Vietnamese economic activity with wet rice production being the
most prevalent. Agriculture employs 38.6% of the population, industry employs
26.7%, and services employ 34.7%. The main industries of Vietnam include electronics,
machinery, steel, food processing, rice, coffee, cashews, seafood, vegetables,
wood industry, textile, footwear, vehicle, and tourism (Economy of Vietnam, Wikipedia).
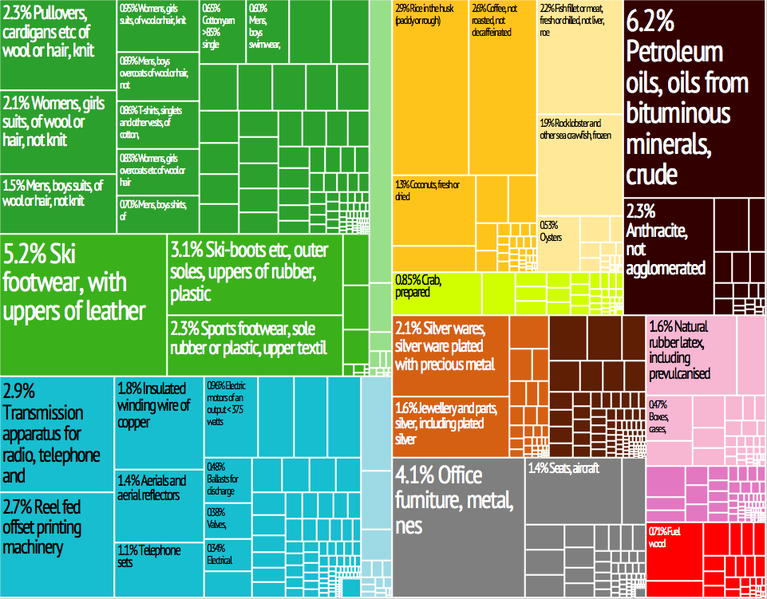
Vietnam
imports goods from other Asian countries; China is the largest importer, with
South Korea following, then Japan, and Thailand. In 2017, Vietnam spent $202.6
billion on imports. Imported goods include machinery and industrial equipment, material
for clothing and shoe production, plastics, cars, metal, chemicals, petroleum
products, and electronics. In 2017, Vietnam exported $214.1 billion in goods.
The biggest importer of Vietnamese exports is the United States, followed by
China, then Japan, and South Korea. Vietnamese exports include textiles,
electronics, footwear, wood products, seafood, steel, crude oil, rice, coffee,
pepper, and transportation products (Economy of Vietnam, Wikipedia).
By
GDP, Vietnam is the 44th largest economy in the world, and 32nd
largest when measured by purchasing power parity (PPP). The estimated GDP of
2019 was $261.637 billion and GDP per capita is $2,740. Unemployment is 2.17%,
with youth unemployment at 6.9%. The estimated public debt of 2017 was 58.5% of
GDP (Economy of Vietnam, Wikipedia).
References
“Vietnam Population.” AloTrip,
www.alotrip.com/about-vietnam-people/vietnam-population.
“World Population Database 2019.” Prb.org, Population
Reference Bureau, 2019, unomaha.instructure.com/files/2501483/download?download_frd=1.
“Vietnam.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 22 Apr.
2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vietnam.
“Climate of Vietnam.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia
Foundation, 26 Mar. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Climate_of_Vietnam.
“Economy
of Vietnam.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 26 Mar. 2020, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Vietnam.
“Chapter 10 Southeast
Asia.” World Regional Geography: Global Patterns, Local Lives, by Lydia Mihelic Pulsipher and Alex Pulsipher, Macmillan, 2010, pp.
597–598.
Submitted by Jennifer Nguyen on April 23, 2020.